
Iran"s mining sector supports agriculture and industry growth. "
Iran is rich in mineral resources, and mining plays a significant role in the country's economy. It possesses substantial reserves of various minerals, including oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, and many others. The mining sector in Iran supports the country's industrial activities by providing essential raw materials. For example, iron ore is mined and used in the steel industry, while copper is extracted for the production of electrical wires and components. Iran has a diverse agricultural sector, producing a wide range of plant products. These include wheat, rice, barley, corn, fruits, vegetables, tea, cotton, and various medicinal plants. The plant products are utilized by different industries in Iran. For instance, wheat and rice are crucial for the food processing industry, while cotton is used in textile and clothing manufacturing. Medicinal plants are processed for pharmaceuticals and herbal products.
Iran's important mines are oil and gas. Iran is the world's fourth-largest oil producer, with 9.4 percent of the world's proven 157 billion barrels of proven oil reserves, and the world's first-largest gas reserves with 18 percent of the world's proven gas reserves, or 33 percent. It has 6 trillion cubic meters, but in total oil and gas reserves, Iran with 379 billion barrels of crude oil equivalent, ranks first in this field. The most important oil areas of Masjed Soleiman Haftgol are Gachsaran Agha Jari and Shahabad (west). Qom oil is also being extracted.
Other important mines of the country are coal mines, metal ores: gold, manganese, chromite, copper, lead, zinc, nickel, cobalt, silver, and iron, chemical minerals: salt, decorative stones, sand. In 1978, the most important and several metal mines in Iran were as follows: lead and zinc, copper, chromite, red soil, and iron ore. Also in the same year, important non-metallic mines and a number that have been exploited are coal, marble, travertine, kaolin, silica turquoise, mineral pumice bentonite, barite, dolomite, refractory, alum, talc, feldspar, gypsum, bicarbonate.
Iranian vegetable products are wheat, barley, rice, corn, chickpeas, beans, mung bean, lentils, tobacco, cotton, hemp, sugarcane, and all fruit trees. Fishing, pearl fishing, wildlife, and poultry farming, silkworm, and bee farming, and mushroom farming are also common. Iranian Industries
The main industries of the country are: oil, gas, petrochemical, steel, textile, chemical, food, automobile, electrical and electronic industries, as well as important handicrafts, household and traditional industries of the country are: carpets and rugs, kilims and pillows, carving, inlaying, and pottery.
Iran's industrial sector encompasses various industries, including manufacturing, petrochemicals, automotive, steel, cement, textiles, and food processing. These industries rely on both mined resources and plant products. For instance, the steel industry requires iron ore and coal from mining operations, while the food processing industry utilizes agricultural products such as wheat, fruits, and vegetables. The petrochemical industry, which is a significant sector in Iran, relies on oil and gas reserves for its feedstock. In some cases, raw materials from mines and plant products are further processed within Iran to add value and create finished products. For example, iron ore mined in Iran is processed into steel, which is then used in various industries and construction projects. Similarly, agricultural products like wheat can be processed into flour, which is used in the baking industry or exported.
-
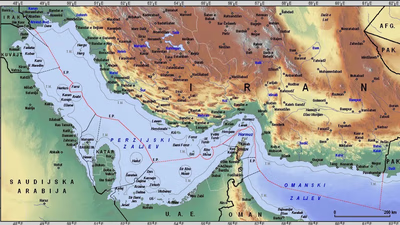
Iran"s transportation infrastructure is vital for trade, featuring an extensive road network, railways, and air routes. Major highways connect key regions, facilitating the movement of goods and passengers. The North-South and East-West Transport Corridors are crucial for linking the Caspian Sea to the Persian Gulf and connecting borders with Turkey and Afghanistan. Iran"s railway system spans over 13,000 kilometers, providing essential links to neighboring countries and supporting both passenger and freight transport. The country boasts several international airports, with Imam Khomeini International Airport serving as the main gateway for global travel. Maritime trade is supported by major ports like Bandar Abbas and Chabahar, which handle significant import-export activities. Additionally, Iran"s oil and gas pipeline network plays a critical role in transporting energy resources domestically and for export purposes. Companies like Beocontrol offer comprehensive transport solutions, ensuring efficient logistics from door-to-door or port-to-port. This robust transportation framework enhances Iran"s position as a key player in regional trade within West Asia.
-

Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, is located in West Asia and is the second-largest country in the Middle East. It shares borders with several countries, including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and Turkey. With a rich history of over 2,500 years, Iran was once the heart of the Persian Empire and has been influenced by various dynasties. The country boasts a diverse culture shaped by Islamic traditions and regional customs. Persian literature and cuisine are notable aspects of its heritage. Iran"s strategic location near the Persian Gulf and the Strait of Hormuz makes it crucial for global oil transportation. The population exceeds 83. 5 million, with Tehran as its capital.
Governed as an Islamic republic with a mixed political system led by a Supreme Leader and an elected President, Iran also has a parliamentary body known as the Majlis. The nation is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas reserves, ranking third among OPEC members. Despite its economic potential, Iran faces challenges from international sanctions and internal corruption. The country is also known for its cultural landmarks like Persepolis and Isfahan"s Naqsh-e Jahan Square. While Iran"s nuclear program has drawn international scrutiny over concerns about weapon development, it maintains that its activities are peaceful. "
-

Iran"s export landscape is dominated by oil and gas, with significant contributions from petrochemicals, metals, and agricultural products. The country is a major player in the global oil market, exporting crude oil and refined products that form a substantial part of its revenue. Additionally, Iran"s well-established petrochemical industry produces a variety of goods such as polymers and fertilizers for international markets. Beyond hydrocarbons, Iran exports metals like iron ore and copper, alongside agricultural products including fruits and nuts. Despite being an oil-rich nation, Iran also imports energy products to satisfy domestic needs. Recent statistics from Bazargan Customs indicate a decline in both exports and imports due to global economic challenges exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. In the first seven months of the year, exports from Bazargan reached over $2 billion but saw significant decreases in both weight and value compared to previous years. The customs director highlighted that machinery, electrical equipment, and consumer goods are among the key imports necessary for supporting local industries. Overall, while Iran has a diverse export portfolio, it faces challenges in maintaining trade volumes amidst fluctuating global conditions.
-

IRICA, the customs authority of Iran, plays a crucial role in regulating trade by managing the flow of goods across borders. It enforces customs laws, collects duties and taxes, and ensures compliance with international agreements. The organization oversees customs procedures at various entry and exit points, conducting inspections and assessments to verify compliance with regulations. Importers and exporters must submit detailed customs declarations to facilitate the assessment of duties and track trade statistics. IRICA collaborates with law enforcement to combat smuggling and other illicit activities while also working on improving customs efficiency through advanced technologies like automated systems. The authority is involved in international relations, engaging in bilateral and multilateral agreements to enhance trade facilitation. Additionally, IRICA administers tariffs based on national laws and international standards, ensuring fair valuation practices for imported goods. By streamlining processes and promoting transparency, IRICA aims to support economic growth through effective trade management.
-

Iran"s economy is significantly bolstered by its rich mineral resources and diverse agricultural sector. The country holds substantial reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, copper, lead, and zinc. Mining activities provide essential raw materials for various industries; for instance, iron ore is crucial for steel production while copper is used in electrical components. Iran ranks as the world"s fourth-largest oil producer and possesses the largest gas reserves globally. Key mining regions include Masjed Soleiman and Gachsaran. Additionally, Iran"s agricultural output includes wheat, rice, barley, fruits, and medicinal plants that support food processing and textile industries. The industrial landscape encompasses sectors such as petrochemicals, automotive manufacturing, textiles, and food processing. These industries rely on both mined resources and agricultural products to create value-added goods.
For example, iron ore is transformed into steel for construction projects while wheat is processed into flour for baking. Overall, Iran"s mining and agricultural sectors are integral to its economic framework.





