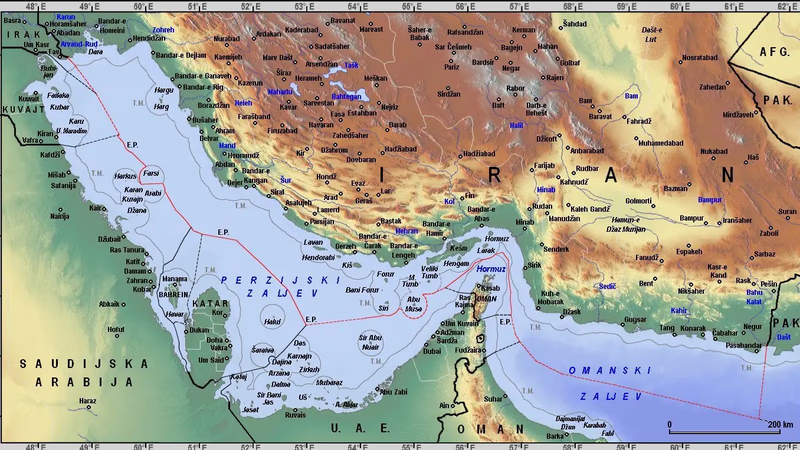
Iran"s transport routes enhance commodity trade in the Middle East. "
Iran has an extensive road network that connects major cities, towns, and rural areas. The road infrastructure includes highways, expressways, and local roads. The major highways in Iran include the North-South Transport Corridor, connecting the Caspian Sea to the Persian Gulf, and the East-West Transport Corridor, connecting the border with Turkey to the border with Afghanistan. The road network facilitates the movement of passenger vehicles, buses, trucks, and cargo transportation across the country.
Roads and vehicles are also important. Railway all over Iran from the Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea (see also Mazandaran Railway) Tehran Railway to Mashhad Railway Tehran to Tabriz Tehran to Kashan, Bandar Abbas Railway to Tehran and Bandar Abbas to Sarakhs Railway which is in operation and Other roads under construction. Highways connect all cities. Shipping routes are in the Caspian Sea, the Sea of Oman, and the Persian Gulf. There are air routes between most of the world's major countries and Iran's top cities.
Beocontrol offers the best solutions for air transport – quickly, safely and conveniently. Whether it’s a charter shipment or a shipment on a regular line, we have the right offer for you. Our team follows the shipment 24/7 and will give you feedback on arrival, as well as the current status of the shipment. The Beocontrol transport services company organizes the door-to-door principle, “from port to port” and “from airport to airport”. Our company will take your goods at the agreed address and arrange rail or road transport to the nearest airport or port. Our team or our associates will organize the goods loading, as well as its landing at the destination, from where it will be delivered to the recipient’s address.
Iran has several international and domestic airports, serving both domestic and international air travel. The Imam Khomeini International Airport, located near Tehran, is the country's main international gateway. Other major airports include Mehrabad International Airport in Tehran and airports in Mashhad, Isfahan, Shiraz, Tabriz, and Kish Island. Iran Air, the national flag carrier, operates domestic and international flights, while other international airlines also serve the country.
Aggregate Container Transportation (LCL) allows for a convenient and reliable transport of smaller quantities of goods in long distances. When the shipment requires only part of the container space, when it is important to the client that the transportation costs are low, and the transit delivery time is less important, the optimal solution is – overseas aggregate container transport (LCL).
Iran's railway system is an important mode of transportation for both passengers and freight. The railway network spans over 13,000 kilometers and is operated by the Islamic Republic of Iran Railways (RAI). The main railway lines run north-south and east-west, connecting major cities such as Tehran, Mashhad, Tabriz, Isfahan, and Shiraz. The railway system also provides international connections, linking Iran with neighboring countries such as Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.
Transport of full containers (FCL) includes a range of activities: from contracting the lease of space on a container ship with a broker and coordinating the delivery of empty containers to the place of loading, through the organization of the filling of the bill, the organization of the export customs clearance and the transfer of the filled container to the shipping agent at the container terminal in the port of delivery , to monitoring the movement of the ship all the way to the port of disembarkation and organization of goods unloading – overseas transport of full containers (FCL) is our specialty.
Iran has access to the Caspian Sea in the north and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in the south. The country has several major ports, including Bandar Abbas, Bushehr, Bandar Anzali, and Chabahar. These ports facilitate maritime trade and transport, handling both imports and exports. Iran's ports serve as important gateways for international trade, connecting to various countries in the region and beyond. Iran has an extensive network of oil and gas pipelines, which are crucial for transporting energy resources within the country and for export. Pipelines transport oil and gas from production sites to refineries, petrochemical complexes, and export terminals. The pipelines connect various regions of Iran, including the oil-rich Khuzestan province and the natural gas fields in the south to major cities and ports.
-
Iran"s transportation infrastructure is vital for trade, featuring an extensive road network, railways, and air routes. Major highways connect key regions, facilitating the movement of goods and passengers. The North-South and East-West Transport Corridors are crucial for linking the Caspian Sea to the Persian Gulf and connecting borders with Turkey and Afghanistan. Iran"s railway system spans over 13,000 kilometers, providing essential links to neighboring countries and supporting both passenger and freight transport. The country boasts several international airports, with Imam Khomeini International Airport serving as the main gateway for global travel. Maritime trade is supported by major ports like Bandar Abbas and Chabahar, which handle significant import-export activities. Additionally, Iran"s oil and gas pipeline network plays a critical role in transporting energy resources domestically and for export purposes. Companies like Beocontrol offer comprehensive transport solutions, ensuring efficient logistics from door-to-door or port-to-port. This robust transportation framework enhances Iran"s position as a key player in regional trade within West Asia.
-

Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, is located in West Asia and is the second-largest country in the Middle East. It shares borders with several countries, including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and Turkey. With a rich history of over 2,500 years, Iran was once the heart of the Persian Empire and has been influenced by various dynasties. The country boasts a diverse culture shaped by Islamic traditions and regional customs. Persian literature and cuisine are notable aspects of its heritage. Iran"s strategic location near the Persian Gulf and the Strait of Hormuz makes it crucial for global oil transportation. The population exceeds 83. 5 million, with Tehran as its capital.
Governed as an Islamic republic with a mixed political system led by a Supreme Leader and an elected President, Iran also has a parliamentary body known as the Majlis. The nation is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas reserves, ranking third among OPEC members. Despite its economic potential, Iran faces challenges from international sanctions and internal corruption. The country is also known for its cultural landmarks like Persepolis and Isfahan"s Naqsh-e Jahan Square. While Iran"s nuclear program has drawn international scrutiny over concerns about weapon development, it maintains that its activities are peaceful. "
-

Iran"s export landscape is dominated by oil and gas, with significant contributions from petrochemicals, metals, and agricultural products. The country is a major player in the global oil market, exporting crude oil and refined products that form a substantial part of its revenue. Additionally, Iran"s well-established petrochemical industry produces a variety of goods such as polymers and fertilizers for international markets. Beyond hydrocarbons, Iran exports metals like iron ore and copper, alongside agricultural products including fruits and nuts. Despite being an oil-rich nation, Iran also imports energy products to satisfy domestic needs. Recent statistics from Bazargan Customs indicate a decline in both exports and imports due to global economic challenges exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. In the first seven months of the year, exports from Bazargan reached over $2 billion but saw significant decreases in both weight and value compared to previous years. The customs director highlighted that machinery, electrical equipment, and consumer goods are among the key imports necessary for supporting local industries. Overall, while Iran has a diverse export portfolio, it faces challenges in maintaining trade volumes amidst fluctuating global conditions.
-

IRICA, the customs authority of Iran, plays a crucial role in regulating trade by managing the flow of goods across borders. It enforces customs laws, collects duties and taxes, and ensures compliance with international agreements. The organization oversees customs procedures at various entry and exit points, conducting inspections and assessments to verify compliance with regulations. Importers and exporters must submit detailed customs declarations to facilitate the assessment of duties and track trade statistics. IRICA collaborates with law enforcement to combat smuggling and other illicit activities while also working on improving customs efficiency through advanced technologies like automated systems. The authority is involved in international relations, engaging in bilateral and multilateral agreements to enhance trade facilitation. Additionally, IRICA administers tariffs based on national laws and international standards, ensuring fair valuation practices for imported goods. By streamlining processes and promoting transparency, IRICA aims to support economic growth through effective trade management.
-

Iran"s economy is significantly bolstered by its rich mineral resources and diverse agricultural sector. The country holds substantial reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, copper, lead, and zinc. Mining activities provide essential raw materials for various industries; for instance, iron ore is crucial for steel production while copper is used in electrical components. Iran ranks as the world"s fourth-largest oil producer and possesses the largest gas reserves globally. Key mining regions include Masjed Soleiman and Gachsaran. Additionally, Iran"s agricultural output includes wheat, rice, barley, fruits, and medicinal plants that support food processing and textile industries. The industrial landscape encompasses sectors such as petrochemicals, automotive manufacturing, textiles, and food processing. These industries rely on both mined resources and agricultural products to create value-added goods.
For example, iron ore is transformed into steel for construction projects while wheat is processed into flour for baking. Overall, Iran"s mining and agricultural sectors are integral to its economic framework.





