
Oman’s hot summers and mild winters impact trade activities.
Summers in Oman are extremely hot, with temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit) in the coastal areas and even higher in the interior regions. The months of June, July, and August are typically the hottest, with very little rainfall during this time. Humidity levels can be high, especially along the coastal regions. Winters in Oman are relatively milder compared to the scorching summers. From November to March, temperatures range from 20 to 30 degrees Celsius (68 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit) during the day, with cooler temperatures at night. The coastal areas experience more moderate temperatures, while the interior regions can still be warm during the day but cooler at night.
Muscat is located on the Arabian Peninsula with long, hot summers like any other Middle Eastern country. Rainfall is very rare in this city, and often falls in the winter months. Muscat has a hot and dry climate with long, very hot summers and short winters. Annual rainfall in Muscat is about 100 mm (4 inches), mostly falling from December to April. In general, it rains in Muscat for a few months, on average, it only rains. The climate is very hot and in summer the temperature is up to 49 ° C. Northerly winds occur in Muscat during the summer months. They are very dusty and start in the morning, but decrease at night. Dust storms are a phenomenon that rarely affects Muscat during the summer months. Oman points, including Muscat, reach from the Mediterranean Sea or North Africa.
The climate of Oman is very hot due to its geographical location, which is clos e to the equator. This is one of the reasons why some people are prevented from migrating because, in general, very cold or tropical countries have fewer fans among those interested in migrating. However, the country has managed to reduce some of its dependence on oil and its sales in recent years, and to upgrade its tourism and fishing industry. Oman's coastal areas, including Muscat, experience the moderating influence of the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. This influence helps keep temperatures relatively lower than in the interior regions, and coastal areas often experience pleasant sea breezes.
Muscat is located in the Arabian Peninsula, with long and warm summers similar to any other Middle Eastern country. The rainfall in this city is very rare, and often drop in the winter months with warm and dry weather, which is long and very hot summer and low winter. Annual rainfall of Muscat is about 100 mm (4 inches), mainly from December to April. In general, precipitation in Muscat is several months, on average, only witnessed rain.
The weather is very hot and in the summer temperature is up to 49 ° C. The north wind occurs in the summer months in Muscat. They are very dusty and begins in the morning, but it's diminished in the morning. The dust is a phenomenon that is rarely affected by Muscat in the summer months. Western, winter to many Oman spots, including Muscat, bring from the Mediterranean or North Africa Sea. Oman's ambition, due to its geographical location, which is close to the equatorial line. The same is one of the reasons why the immigration of some people is, in general, very cold or tropical countries have fewer fans between immigration enthusiasts. Nevertheless, the country has succeeded in reducing its dependence on its oil and sell its tourism and fishing industry in recent years.
Oman receives very little rainfall, particularly in the interior and desert regions. The coastal areas receive slightly more precipitation, mainly during the winter months. The northern part of the country, including Muscat, tends to receive more rainfall compared to the arid interior and southern regions. Salalah, located in the southern part of Oman, experiences a unique monsoon season called the Khareef, during which it receives a significant amount of rainfall and turns lush green. In the southern part of Oman, particularly in the Dhofar region, a unique climatic phenomenon known as the Dhofar winds occurs. These winds blow from the southern hemisphere and bring moisture-laden air, resulting in the Khareef season. The Khareef season, which typically occurs from June to September, brings cooler temperatures and abundant rainfall to the region, transforming the landscapes into lush greenery.
-

Oman is predominantly an Islamic country, with the majority of its population practicing the Ibadi sect, known for its moderation and tolerance. Arabic is the official language, but English is widely spoken, especially in urban areas. Other languages such as Baluchi and Hindi are also common due to historical ties and trade. The cultural practices of Oman reflect its Islamic heritage, with traditional clothing like the Deshdashe for men and hijabs for women being prevalent. Understanding Omani customs is essential for visitors to enhance communication and appreciation of local traditions. The coexistence of various Islamic sects, including Shiites and Sunnis, contributes to a rich cultural tapestry where significant religious occasions are observed collectively. This cultural insight is vital for those engaging in trade or business networking in Oman, as it fosters better relationships with local partners. The country"s unique blend of tradition and modernity makes it an attractive destination for both tourism and commerce. "
-

Exporting goods to Oman requires meticulous documentation, including a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin. Each product must be classified under a specific HS code to determine applicable customs duties and regulations. It is crucial to identify and declare the correct HS code when exporting. Oman has strict regulations regarding prohibited and restricted items, which may include narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit goods. Certain goods may also require export permits or licenses, particularly those related to sensitive technologies or military equipment. Engaging a customs broker or freight forwarder experienced in Omani regulations can facilitate compliance with customs procedures. Oman boasts several key ports such as Qaboos Port and Sohar Port, which are vital for trade operations. The average customs tariff for agricultural exports is around 4.
7%, with some commodities exempt from duties. Additionally, value-added tax (VAT) applies to most goods in Oman. Businesses looking to streamline their operations can benefit from the Authorized Economic Operator program that expedites customs processes for compliant companies. Proper packaging and labeling according to international standards are essential for successful exports.
-
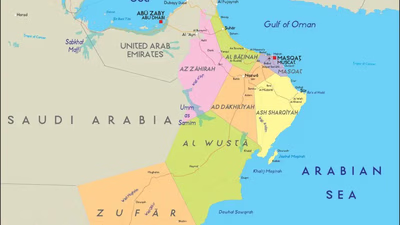
Oman, located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, shares borders with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen. Its capital, Muscat, is a vibrant city known for its rich history and cultural attractions. The geography of Oman features rugged mountains, vast deserts like the Wahiba Sands, and a stunning coastline along the Arabian Sea. Muscat serves as a key maritime hub with Port Sultan Qaboos facilitating trade and tourism. The city blends traditional charm with modern developments, offering attractions such as the Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque and Royal Opera House. Oman"s climate is characterized by hot summers and milder winters, with high humidity along the coast. The local culture is deeply rooted in tradition, reflected in its cuisine and hospitality. Oman actively promotes tourism to showcase its natural beauty and heritage, making it an appealing destination for travelers seeking adventure and cultural experiences. "
-

Oman is strategically positioned within the Gulf Cooperation Council, collaborating closely with Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait on economic and security matters. Its relationships extend globally, notably with the United States and the United Kingdom, focusing on trade and defense. China stands out as Oman"s largest trading partner, accounting for a significant portion of both exports and imports. Other key partners include India, Japan, and Saudi Arabia. Oman’s import landscape features machinery, fossil fuels, steel products, and food items. The country is enhancing its infrastructure to boost trade capabilities and attract foreign investment. Recent years have seen a surge in construction-related imports as Oman develops new economic zones. Iranian traders are also active in exporting construction materials to Oman.
The nation’s geographic location near the Indian Ocean positions it as a vital regional trade hub. Oman"s proactive approach to fostering international partnerships aims to strengthen its economic standing in West Asia.
-

Oman"s climate is characterized by extremely hot summers, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F) in coastal areas and even higher inland. The hottest months are June, July, and August, with minimal rainfall and high humidity along the coast. Winters are milder, ranging from 20 to 30°C (68 to 86°F) during the day, with cooler nights. Muscat experiences very little annual rainfall, averaging about 100 mm (4 inches), primarily from December to April. Dust storms can occur during summer months due to northerly winds. Oman"s geographical location near the equator contributes to its hot climate, which can deter migration compared to cooler countries. However, Oman has diversified its economy by reducing oil dependence and enhancing tourism and fishing industries. Coastal areas benefit from the moderating effects of the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman, leading to more pleasant temperatures than the interior regions. The southern region of Dhofar experiences a unique monsoon season known as Khareef from June to September, bringing significant rainfall and transforming landscapes into lush greenery.





