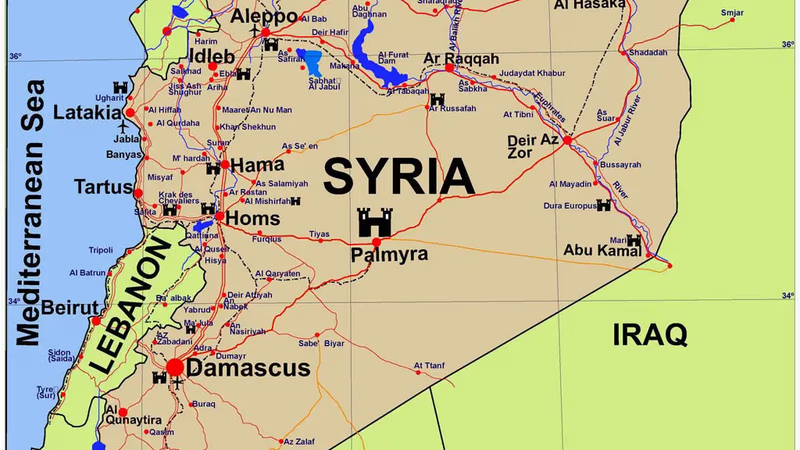
Syria"s diverse landscapes: mountains, rivers, and trade routes. "
Syria is a country located in the Middle East, bordered by Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, Israel to the southwest, and Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. It has a diverse geography that includes various landscapes and features. Along the western edge of Syria lies a narrow coastal plain that stretches from north to south. This region is fertile and highly populated, with cities like Latakia and Tartus located on the coast. Moving inland from the coast, Syria is characterized by several mountain ranges. The Anti-Lebanon Mountains form the country's western border with Lebanon. The mountainous region includes the Jebel al-Aalaq, Jebel Ansariye, and Jebel el-Sheikh ranges.
Apart from the Euphrates River, Syria has a few other significant water bodies. Lake Assad, a reservoir created by the Tabqa Dam on the Euphrates, is the largest lake in the country. The Orontes River flows through the western part of Syria before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. Syria's geography has played a significant role in its history and cultural development. The different regions of the country have distinct climates, resources, and agricultural potential, influencing settlement patterns and economic activities.
It is located in West Asia, north of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East, and east of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Lebanon and Palestine to the west, Iraq to the east, and Jordan to the south. Syria's geography includes mountain ranges in the west and steppes in the interior. The Syrian desert is located in the east and the Druze mountain range in the south of the country. The Euphrates River has divided the Syrian desert. The reservoir of the dam, which was built on the Euphrates in 1973, is called Lake Assad and is currently the largest lake in Syria.
Syria's highest point is Mount Jabal al-Sheikh, 2,814 meters (9,232 feet) on the Lebanese border. Semi-arid steppe zones, nestled between the wet shores of the Mediterranean on one side and the desert on the other, cover about three-quarters of the country. These steppe zones host hot, dry winds blowing through the desert.
Syria's diverse nature, with its mountains, valleys, deserts, rivers, and access to open waters, has had a tremendous impact on the country's industries and agriculture. The Syrian economy is based on the three pillars of industry, agriculture, and trade, and we must not forget the oil and gas industry, as well as the tourism industry. The Syrian economy faced many crises in the 1990s that could overshadow the country's future, and at a glance, they can be summarized in three main sections.
- Oil is a perishable stock and due to its high price fluctuations and the trend of declining underground reserves, it cannot be considered as the main source of income.
- The average annual population growth in Syria is 3.3%, which is above the global average. This trend has increased the labor force and forced the country to make huge investments in education, health, and the social security system.
- Trade opening, which is due to Syria being in the Free Trade Zone of the Arab countries or due to cooperation with the European Union or joining the World Trade Organization, will have a great impact on Syrian industry because many Syrian factories and industrial centers Government support will not be able to withstand this opening.
Syria is divided into fourteen provinces. Each province is divided into 60 counties (in Arabic: region), and each county into smaller sections (in Arabic: district). Damascus is the capital of Syria and the second-largest city in the country. The city of Aleppo in the north is the largest in Syria. The cities of Latakia and Tartus are the largest and main ports on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. The Syrian economy is known as a state economy. The lack of strong financial resources and infrastructure in the private sector, as well as government interference in the economy, has put the country in a difficult economic situation.
To the east of the mountains, the Syrian Desert, also known as the Badiyat ash-Sham, dominates the landscape. It is a vast arid expanse of rocky and sandy terrain, sparsely populated, and home to several oasis towns. The Euphrates River, one of the most important rivers in the region, runs diagonally across Syria from northeast to southwest. The river valley is a fertile region that supports agriculture and human settlements. In the northern part of Syria, there are extensive plateaus such as the Aleppo Plateau and the Homs Plateau. These areas have relatively flat terrain and are agriculturally productive.
-

Goods imported into Syria are subject to customs duties based on valuation and tariff rates set by the Syrian Customs Authority. Import and export controls are enforced for national security, public health, and environmental protection, requiring compliance with licensing and permit regulations. The Harmonized System (HS) is used for customs classification, necessitating accurate tariff code usage by importers. Temporary importation is allowed under specific conditions, requiring guarantees for potential duties. Customs clearance involves documentation submission and payment of fees. Non-compliance can lead to penalties such as fines or legal consequences. Accurate customs declarations are essential, as the Syrian Customs Authority may verify declared values or use alternative methods if necessary. Syria participates in international trade agreements that may offer preferential treatment for certain goods.
Various entities, including foreign project companies and international organizations, can import goods under specific conditions, often requiring re-exportation after use. Tourists can bring personal vehicles temporarily without tax obligations. Factories can import raw materials tax-free if they export their products. The customs valuation process relies on transaction value but may involve audits and inspections to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
-
Syria"s geography is diverse, featuring coastal plains, mountain ranges, and deserts. The western coastal region is fertile and densely populated, with key cities like Latakia and Tartus. Inland, the Anti-Lebanon Mountains define the western border, while the Euphrates River and Lake Assad are significant water bodies. The country"s varied landscapes influence its agriculture and economic activities. Syria"s economy relies on industry, agriculture, trade, oil, and tourism but faces challenges due to high population growth and fluctuating oil prices. Trade liberalization through regional agreements may impact local industries as they adapt to increased competition. The capital city of Damascus is central to trade activities, while Aleppo serves as a major urban center. Overall, Syria"s geographical features play a crucial role in shaping its economic landscape.
-

The Port of Latakia is Syria"s primary seaport, crucial for maritime trade, handling container shipping, general cargo, and bulk cargo. The Port of Tartus also plays a significant role, mainly dealing with bulk cargo like petroleum and agricultural products. Despite the ongoing civil conflict since 2011 impacting infrastructure, efforts are underway to enhance port facilities and restore trade connectivity. Historically, Syria was a vital transit point for goods between the Persian Gulf and Europe, with around 30,000 shipments annually before the conflict disrupted this flow. The Syrian Free Zones offer strategic advantages for commercial activities, including tax exemptions and infrastructure support. These zones are located in key areas such as Latakia and Damascus International Airport. Coastal shipping routes connect Syria"s cities, facilitating domestic trade alongside international operations. Ports are essential for importing and exporting various goods across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
-

The Central Bank of Syria (CBS) oversees the country"s banking sector, ensuring compliance with monetary policies and regulations. Banks must obtain licenses from the CBS, which sets capital requirements and governance standards. Foreign exchange regulations are in place to manage currency flows and cross-border transactions. While foreign banks cannot establish branches in Syria, joint ventures with a majority Syrian ownership are permitted. The banking system is undergoing reforms to allow private banks to operate alongside state-owned institutions. Taxation in Syria includes corporate income tax rates ranging from 10% to 45% and payroll taxes between 5% and 12. 5%. Banks must maintain adequate capital levels and adhere to prudential regulations for stability.
Consumer protection measures are also included in banking laws, ensuring fair practices and transparency for customers. Additionally, banks are required to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations, implementing customer due diligence and reporting suspicious activities. "
-

Syria"s recent ban on Turkish imports has opened opportunities for Iranian exporters, particularly in sectors like energy, construction, medical equipment, and food industries. The reconstruction efforts in Syria present a significant market for Iranian goods, given the country"s large consumer base of 22 million people. With Iran"s competitive pricing and political influence in the region, Iranian products are well-positioned to meet the demands of the Syrian market. The absence of Turkish and Egyptian competition further enhances Iran"s prospects in Syria. Additionally, the geographical location of Syria allows access to European and African markets, creating further trade opportunities for Iranian businesses. Identifying new markets and facilitating exports will be crucial for economic development in both countries. The potential for technology transfer alongside exports can strengthen international trade relations and support industry growth.





