
Bahrain"s strategic location boosts Middle East trade opportunities. "
Bahrain's location in the Persian Gulf makes it an important hub for trade between the Middle East, Asia, and Europe. It serves as a gateway between the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and the rest of the world. Bahrain's proximity to Saudi Arabia, one of the largest economies in the Middle East, further enhances its economic importance. Bahrain has established itself as a leading financial center in the region. It is home to the Bahrain Financial Harbour, which houses numerous international and regional banks, investment firms, and insurance companies. The country has a well-regulated and business-friendly financial system, attracting foreign investment and fostering economic growth.
Like many countries, Bahrain faces economic challenges, including fiscal sustainability, unemployment, and the need for continued economic diversification. However, the government has implemented reforms to address these issues and has sought to attract foreign investment through various initiatives. The growth rate of GDP in Bahrain is about -2.49, the country's ranking in terms of gross fixed capital has grown by more than 33%. The situation of GDP in agriculture in Bahrain is about 8.93 million in the field of construction, 234.74 million, and from the mine 553.03 million. As it is known, in Bahrain, the housing situation and the structure are also seen in a safe situation, and the security of the structure in Bahrain has increased by about 30% than before.
Bahrain has more than 23 percent of GDP from public transportation, a 47 percent increase in welfare services, while the country ranks 89th in the world in terms of welfare services. And the government of this country values citizenship. Bahrain in terms of trade balances is -320.30 million dinars and the current account balance in this country is -834.70 million dinars. Bahrain ranks more than 80% in terms of imports and exports, with 4.70 tonnes of gold reserves. The turnover situation in Bahrain has grown by about 96% and crude oil production in this country is estimated at 40.00 BB. Bahrain has generally had good approaches to credit assessments. Food inflation in Bahrain is about 1 percent and the consumer price index for transportation based on index points is 100.00 and the GDP adjustment coefficient based on index points is 107. Bahrain's situation in the stock market has also grown a lot.
The political structure in Bahrain is a constitutional monarchy, as the constitution was adopted in 2002. The legal system in this country seriously includes the Islamic sections. The legislature in Bahrain has two houses, the Shura and the House of Representatives. Both parliaments in this country have 40 members and all members of the parliament are elected by the Amir and all members of the House of Representatives are elected by direct popular vote. There are about 15 political parties in the country, including religious, liberal, leftist, and Ba'athist. The political situation in this country is similar to a dictatorship, but the people of Bahrain do not get involved in politics.
Although Bahrain's economy has become more diversified, the oil and gas sector still plays a significant role. Bahrain has limited oil reserves but has been exploring offshore fields to increase production. The country has also invested in natural gas extraction and has plans to develop its liquefied natural gas (LNG) industry. Bahrain has invested in developing its logistics and transportation infrastructure. It is home to the Bahrain International Airport, which serves as a major air cargo hub in the region. The country also boasts a well-connected road network and a modern seaport, attracting international shipping and logistics companies.
Bahrain has made efforts to diversify its economy beyond oil and gas, focusing on sectors such as financial services, tourism, logistics, and manufacturing. The government's Economic Vision 2030 aims to transform Bahrain into a sustainable and globally competitive economy. The country has invested in infrastructure development, education, and innovation to support economic diversification. Bahrain has a liberal trade regime and actively promotes international trade. It is a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). Bahrain has also signed several free trade agreements, including the United States-Bahrain Free Trade Agreement, which has boosted bilateral trade between the two countries.
-

Bahrain, strategically located near Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, is an archipelago with a rich cultural and economic landscape. The capital city, Manama, serves as a hub for trade and tourism. The economy has transitioned from traditional pearl diving to a robust petroleum export sector, contributing significantly to government revenue. Bahrain"s climate is characterized by hot summers and mild winters, influencing its lifestyle and economic activities. The country has a diverse population of approximately 1. 5 million people who predominantly speak Arabic and practice Islam. Cultural practices are deeply rooted in Islamic traditions, with specific customs observed during Ramadan. Bahrain"s legal framework reflects its religious values, with strict laws governing respect for the flag and religious customs.
Understanding these cultural nuances is essential for businesses engaging in trade within the region. As Bahrain continues to develop as a B2B marketplace in West Asia, it offers opportunities for verified exporters and importers to connect through regional product listings and supply chain solutions.
-

Bahrain"s strategic location in the Persian Gulf positions it as a vital trade hub connecting the Middle East, Asia, and Europe. It serves as a gateway for trade among Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and beyond. The nation has developed into a prominent financial center, hosting the Bahrain Financial Harbour, which attracts numerous international banks and investment firms. Despite facing economic challenges such as fiscal sustainability and unemployment, Bahrain"s government is implementing reforms to attract foreign investment. The country"s GDP growth rate is approximately -2. 49%, with significant contributions from agriculture, construction, and mining sectors. Bahrain"s trade balance shows a deficit of -320. 30 million dinars, yet it maintains a strong import-export ranking of over 80%.
The economy is diversifying beyond oil and gas, focusing on sectors like financial services, logistics, tourism, and manufacturing under its Economic Vision 2030 initiative. Infrastructure investments have enhanced logistics capabilities with a modern seaport and an international airport serving as key air cargo hubs. Bahrain"s liberal trade policies and membership in the WTO facilitate international trade relations. "
-

Bahrain"s economy has evolved from its traditional reliance on pearls to a diversified structure with significant contributions from tourism, petroleum, and aluminum production. The country exports 60% of its petroleum products, which constitute about 30% of its GDP. Recent growth in trade and services has reached 64%, while the construction sector contributes approximately 17%. Bahrain is recognized for its aluminum production, ranking first in the Middle East and fifth globally. The agricultural sector has also seen a modest increase of 6%. Despite limited oil and gas resources, Bahrain"s financial landscape is robust, with a capital turnover growth of 96% and a current account balance exceeding 12%. The inflation rate remains low at 0. 20%, indicating economic stability.
Bahrain"s trade processes align with modern standards, facilitating imports primarily from Japan and exports to Saudi Arabia and the United States. The country’s cultural practices, including those during Ramadan, reflect its Islamic heritage while contributing to the tourism sector"s growth. Overall, Bahrain demonstrates a strong capacity for economic development through diversification and modernization.
-
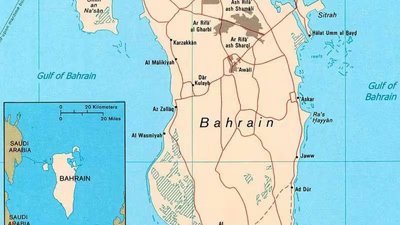
Bahrain"s capital, Manama, serves as a key industrial hub and a popular tourist destination. The city boasts excellent educational facilities, making it attractive for students. Muharraq is notable for its historical architecture, preserved by government efforts. Al-Riffa offers diverse experiences with its historical sections and mountainous areas. Aali is recognized for its private universities and scenic beauty, appealing to the youth. Sitra stands out as a major economic center with significant global recognition. Hamad is known for its tourism potential, supported by government initiatives. Isa is characterized by its indigenous population and a unique work environment, despite some social challenges.
Other cities like Al-Malikiyah, Al-Badi"a, and Al-Had contribute to Bahrain"s diverse urban landscape. The corporate tax rate in Bahrain is zero for foreign investors, enhancing the business environment. The social security rates are competitive, and the sales tax exceeds 5%. Trade in Bahrain is thriving, particularly among Iranian companies in services and clothing sectors. Recent immigration trends indicate a 22% increase in residents choosing Bahrain as their home, reflecting the country"s improving economic conditions.
-

Bahrain has made significant strides in its export sector, particularly in aluminum foil production, leveraging organic raw materials. The country"s educational advancements in medicine and laboratory materials have contributed to its economic growth. Enhanced security measures have improved the living conditions for expatriates, fostering a stable environment for business. Urban transportation has also seen improvements, with consistent ticket pricing and increased safety measures. Despite a 20% decrease in re-exports during the second quarter of 2020, Bahrain remains a key player in regional trade, with Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and China being major partners. The trade balance showed slight improvement with a deficit of BD485 million. Key exports include mineral fuels, machinery, electrical equipment, and various consumer goods. Iran is a notable trading partner for Bahrain, exporting items like flooring and sweets.
However, challenges such as currency return issues and raw material supply persist for exporters. Overall, Bahrain"s strategic location and investment in infrastructure position it as an essential hub for trade in the Middle East.





