
Kuwait"s trade platform showcases verified exporters and importers. "
Kuwait is a major exporter of petroleum and petroleum-related products. Crude oil and refined petroleum products, including gasoline, diesel, and liquefied natural gas (LNG), form a significant portion of the country's exports. The majority of Kuwait's oil exports are shipped to countries in Asia, particularly China, India, South Korea, and Japan. Additionally, Kuwait exports other goods such as chemicals, fertilizers, plastics, and some manufactured products.
Trade Agreements: Kuwait is a member of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), which promotes economic integration and trade cooperation among its member countries. The GCC has implemented a customs union and is working towards establishing a common market. Kuwait has also signed bilateral trade agreements with several countries to enhance trade relations and facilitate investment. Due to its significant oil exports, Kuwait has traditionally maintained a trade surplus, with export revenues exceeding import expenditures. However, fluctuations in oil prices and global market conditions can affect the balance of trade and Kuwait's trade surplus.
Kuwait does not have a large volume of non-oil exports. Most of the country's exports are based on exports of oil and fossil fuels. Most of Kuwait's exports go to countries such as India, the United Arab Emirates, Iraq, Pakistan, Oman, and China. According to the latest global data, Kuwait exported $ 66 billion worth of goods to various countries in 2018, which is a jump of about 20% compared to the previous year. This year, oil and fossil fuels account for about 92 percent of Kuwait's exports. Organic chemicals, fertilizers, plastics, minerals, aluminum, and precious stones are each next with a small percentage. These figures show that oil and fossil fuels are the mainstays of Kuwait's economy and that the country needs to import many goods.
Kuwait engages in trade with countries across the globe. Major trading partners vary depending on the specific commodities being traded. In terms of petroleum exports, Asian countries, particularly China and India, are significant customers. Kuwait also has trading relationships with countries in Europe, the Middle East, and North America. Kuwait has established free trade zones to promote international trade and attract foreign investment. The most notable free trade zone is the Shuwaikh Free Trade Zone, located near the Port of Shuwaikh. These zones provide various incentives, such as tax exemptions and streamlined customs procedures, to encourage foreign businesses and facilitate trade.
Because the Persian Gulf economy is a single product, it meets many of its needs, including products and foodstuffs, through imports. Statistics show that China and the United States are Kuwait's main partners in the import debate. Among Kuwait's neighbors, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates also export a significant portion of their goods to Kuwait. Meanwhile, the emptiness of Iranian goods in Kuwait is quite felt. The map below shows Kuwait's main partners in the import debate. World Trade Organization (WTO) data for 2018 show that Iran does not have a large share of Kuwait's imports. According to the same data, among the imported goods of Kuwait, the names of some goods are more prominent, which indicates the import needs of Kuwait. In the following, we will refer to the main import groups of this country.
Kuwait imports goods in many fields. However, this list may change slightly over the years. But on average, some products are often part of Kuwait's regular import needs. Other import needs of Kuwait include plastic products, medical equipment, construction materials, and many other products. However, usually, each country exports certain goods to Kuwait. The United States, for example, plays a major role in supplying food to Kuwait. While other countries may focus more on exporting other products to this Persian Gulf country. Statistics show that in recent years, the amount of Iranian goods exported to Kuwait has always fluctuated slightly. But this statistic has suddenly jumped significantly in 2018.
This year, $ 358 million worth of goods were exported from Iran to Kuwait. Although this amount of goods is not much compared to the total imports of Kuwait from other countries, it shows a very significant growth compared to previous years. In 2017, the export of Iranian goods to Kuwait was less than $ 200 million. The chart below shows the number of Iranian goods exported to Kuwait in recent years. In 2018, Iran exported more than $ 350 million worth of goods to Kuwait. The chart above shows that there have been two significant jumps in the export of Iranian goods to Kuwait, the first being in 2013 and the second in 2018. It should be noted that statistics for 2009 and 2012 were not available.
Kuwait imports a wide range of goods to meet its domestic needs and support various industries. Major import categories include machinery and equipment, vehicles, food products, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, electrical machinery, textiles, and consumer goods. Key trading partners for Kuwait's imports include China, the United States, Germany, India, and the United Arab Emirates. The country also imports significant amounts of food products to meet its domestic consumption requirements.
-

Kuwait"s trade landscape is heavily dominated by petroleum exports, which account for approximately 92% of its total exports. The primary markets for these oil exports are Asian countries, notably China and India. In addition to oil, Kuwait also exports chemicals, fertilizers, and plastics. The country benefits from its membership in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), which fosters economic integration and trade cooperation among member states. Kuwait has established free trade zones, such as the Shuwaikh Free Trade Zone, to attract foreign investment and streamline customs processes. Despite a strong export economy, Kuwait relies on imports for many goods, including machinery, food products, and medical equipment. Major import partners include the United States, China, Germany, and India. Recent data indicates a notable increase in Iranian goods exported to Kuwait in 2018, highlighting shifts in trade dynamics within the region. Overall, while oil remains the cornerstone of Kuwait"s economy, the country is actively engaging in diversifying its trade relationships and enhancing its import capabilities.
-

Kuwait, located in the northeastern Arabian Peninsula, is bordered by Iraq and Saudi Arabia. With a population of approximately 4. 3 million, it features a mix of Kuwaiti citizens and expatriates. The capital, Kuwait City, serves as the political and economic hub. While not a major tourist destination, Kuwait offers attractions like the Kuwait Towers and Grand Mosque. The country has a strong economic presence in the region due to its strategic location and access to international waters. It is known for its high-value currency, the Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD), and well-developed infrastructure including roads, airports, and seaports. Kuwait"s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports but is diversifying into finance, real estate, and trade sectors.
The cultural landscape is influenced by Islamic traditions and Arab customs, with a significant expatriate community contributing to its demographic diversity. Understanding Kuwait"s market dynamics can benefit businesses looking to engage in import-export activities.
-

Kuwait"s economy is heavily influenced by Islam, which shapes its cultural and legal frameworks. The Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) is the official currency, known for its high value linked to the oil sector. Approximately 70% of the population are Sunni Muslims, with a significant emphasis on charitable giving through zakat. The economy relies predominantly on oil exports, accounting for about 85% of government revenue. Despite this dependency, Kuwait is pursuing economic diversification to reduce reliance on oil and enhance sectors like finance and tourism. The country has implemented fiscal reforms in response to fluctuating oil prices, aiming to stabilize its economy. Agriculture plays a minimal role in GDP, making Kuwait a major food importer. The stability of Kuwait"s economy attracts global business actors, fostering a favorable environment for trade and investment.
Additionally, Islamic finance is prominent in Kuwait, offering Sharia-compliant financial products that align with religious principles. Religious tourism also contributes to the economy as visitors come to explore its historical Islamic sites.
-

Kuwait"s economy is heavily reliant on crude oil exports, which constitute 90% of its GDP and 75% of government revenue. The aftermath of the Gulf War in 1990 severely impacted its economic structure, leading to significant foreign investment efforts to revitalize the economy. Key exports to Kuwait include mineral products like gypsum and cement, iron and steel, live animals, food products, vegetables, fish, fruits, and building materials. The country has a relatively high per capita income due to its small population and substantial GDP. Despite economic challenges post-war, Kuwait has maintained a low inflation rate and a diverse import market for food and construction materials. The government has sought advice from international financial institutions to implement economic reforms focusing on privatization and tax increases. Kuwait"s strategic location enhances its role as a trade hub in the region, with major trading partners including the US, Japan, South Korea, and several European nations.
-
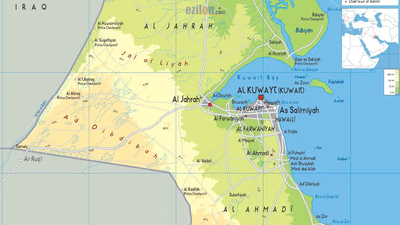
Kuwait"s ports play a crucial role in its trade landscape, with the Port of Shuwaikh being the largest and busiest, handling a variety of commercial cargo. The Port of Shuaiba follows as the second-largest, focusing on bulk cargo such as petroleum products and chemicals. Bubiyan Port, currently under development, aims to become a significant transshipment hub with advanced facilities. Al-Ahmadi Port is dedicated to oil exports, while other ports like Al-Zour and Doha serve specific functions in the oil and light goods sectors. The strategic location of these ports enhances Kuwait"s attractiveness for global traders. Import regulations require licenses from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, ensuring that only registered importers can operate within the country. This regulatory framework supports a stable trade environment, fostering connections between local exporters and international markets.
-
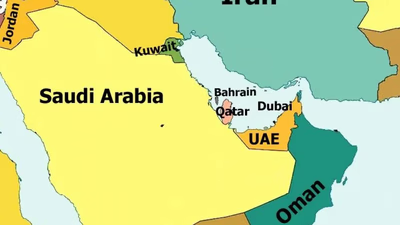
Kuwait, located in West Asia, shares borders with Saudi Arabia and Iraq, and has a coastline along the Persian Gulf. Despite its small geographical size of over 17,000 square kilometers, Kuwait has a rich history and complex identity. The country was founded by Sheikh Barak ibn Gharir al-Hamid in the early 18th century and has evolved into a significant player in regional trade. Approximately 60% of its population are Arabs, with a notable Asian demographic as well. The official language is Arabic, while English is widely spoken due to historical influences. Kuwait"s climate is predominantly hot and dry, necessitating substantial imports of food and water. The nation has made strides in improving its agricultural practices through greenhouses and other innovations. Politically, Kuwait operates as a sheikhdom with a parliamentary system that allows for greater openness compared to some neighboring countries.
Since gaining independence in 1961, it has maintained stability and fostered international relations despite historical territorial disputes with Iraq. Today, Kuwait stands as one of the safest countries in the region, making it an attractive hub for trade and business networking. "






