Natural Stones Prices in Jordan
Jordan in West Asia and tangent to the Gulf of Aqaba is in the best location for trading. Marble is widely used in the Middle East for its elegance and beauty. Jordan has faced economic challenges, including high unemployment rates and public debt. Building stones should be light and should not be technically heavier than a certain limit. The type and quality of the packaging are very important in determining the health of cargo. Travertine is very popular among people for building and is also a good stone for the flooring
Add your import and export orders to this list
Warning: Undefined variable $formTitle in /home/anbar/domains/anbar.asia/anbar/inc/html/desktop/orderform.php on line 10
Warning: Undefined variable $marketName in /home/anbar/domains/anbar.asia/anbar/inc/html/desktop/orderform.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined variable $location in /home/anbar/domains/anbar.asia/anbar/inc/html/desktop/orderform.php on line 12
If you want to trade in the , please join in Anbar Asia. Your order will be shown here, so the traders of contact you
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy and parliament also plays an important role in the country. Natural stones are commonly used for flooring in both residential and commercial buildings. Jordan has always pursued a pro-Western foreign policy and has long had close ties with the United States and Britain. Marble is one of the calcareous stones and due to its internal impurities, it has a cream to gray colors
- Jordan Quartzite Market
- Jordan Granite Market
- Jordan Sandstone Market
- Jordan Marble Market
- Jordan Travertine Market

Based on this, marble reserves are estimated at 2.16 billion, granite at about 1.5 billion tons, travertine at about 450 million tons, and marble at 44 million tons. The number of decorative Natural Stones extracted in the country last year was 10.6 million tons. The amount of extraction of decorative stones in the country last year was 10.6 million tons.
Read More ...
Building stones should be light. The buildings should not be technically heavier than a certain limit. Therefore, according to the materials and bearing of each structure, the appropriate stone should be used. Some building stones are very heavy and strong and some are light. Of course, this lightness is a reason for less strength than heavier stones.
Read More ...
Marble is often associated with prestige, luxury, and grandeur. In West Asia, marble has cultural and symbolic significance, representing power, wealth, and architectural excellence. Its use in religious buildings, palaces, and important public structures reflects the region's cultural heritage and artistic achievements.
Read More ...
Its weight is high and its use puts a dead load on the building. Installation of this stone is time consuming due to the use of mortar for adhesion. This stone is not thermal and acoustic insulation, thus leading to energy loss in the building. Granite adhesion to mortar is not ideal. For this reason, its use as a paving stone has recently been banned because it is likely to fall.
Read More ...
Marble can be resistant to most rock against the environmental conditions such as humidity, heat and cold. The rock also has good resistance against rain and acidic rain. Stone structure is in a way that is rarely infected, and keep its beauty for a long time.Other features marble are as follows:
Read More ...
Moreover, travertine is considered a sustainable choice in architecture and design. It is a natural stone that is widely available, and its extraction and production processes have become more environmentally friendly over the years. Additionally, travertine has excellent thermal properties, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
Read More ...
It can be said that it is a stone between marble and lime found in abundance near hot springs, especially limestone caves. The large cavities in the texture of this rock, as mentioned, are caused by gases trapped in hot water and make the surface of the rock, not polished and slippery, and a good choice for the floor of places that experience high humidity.
Read More ...
Travertine stones are usually available in ivory white or completely white and caramel. More common colors are naturally more economical as well, while stones with rarer colors are often much more expensive.
Read More ...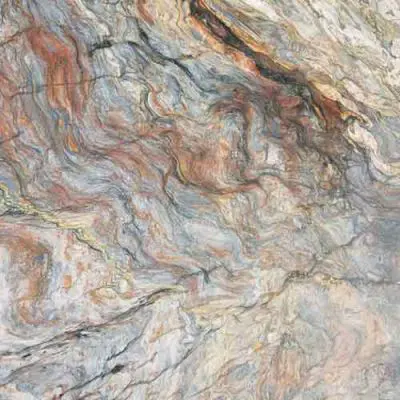
When the sandstone is transformed into quartzite, the quartz grains that were already there are crystallized again along with the cementitious material that was previously present in the sandstone, and the new quartz crystals are fused together. Most or all of the old sandstone texture and sedimentary structure will be completely removed by metamorphism and replaced by a new structure.
Read More ...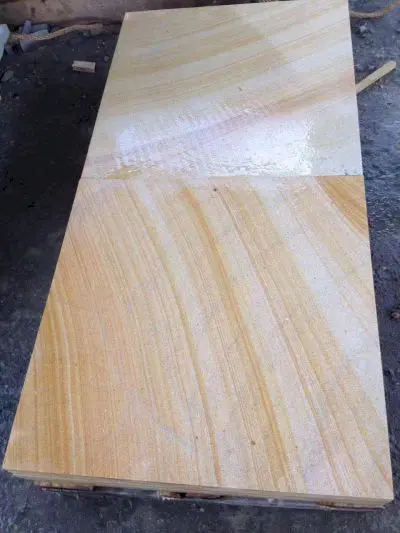
The formation of rocks, which are sandstones, is such that they are permeable to water and their porosity is such that they can hold large amounts of water, which makes them precious watersheds. Fine-grained watersheds such as sandstones are more prone to filtering contaminants from the surface than rocks such as limestone and other rocks formed by seismic activity.
Read More ... Phosphates are among Jordan’s most abundant natural resources, and phosphate mining is one of the leading industries. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this image of a Jordanian phosphate mine on September 17, 2005. According to the Jordanian Natural Resources Authority, phosphate formations cover roughly 60 percent of the total area, and reside mostly in a 300-kilometer- (185-mile-) wide swath that passes north to south through the country. Jordanian granitic rocks (JG) are highly distributed and available in huge quantities in south Jordan, Aqaba area. Granite in south Jordan (JG) is belonging to Aqaba granite complex. This study has been carried out to investigate geological and engineering properties of JG from Aqaba vicinity, south Jordan, in addition to identify and classify the different granitic rocks. Huge sources of granite and granodiorite rocks are distributed over random spots in Agaba complex, southern part of Jordan. [5] had published the first geological map of Trans Jordan. [6] developed the first detailed studies on the basement rocks, defined the Aqaba Granite Complex, and published three scale maps of 1:250,000 for the Transjordan Rift to accompany the first comprehensive report on the geology of Jordan by [3] . German Geological Mission (GGM) [7] , produced geological maps of scale 1:100,000 for South-West Jordan, where six sub-units of the crystalline basement rocks were characterized. Final report has included surveys over the entire basement exposed in South Jordan―the far north of the Shield. The geophysical studies were conducted on the basement rocks in South Jordan by aerial geophysical survey (magnetic, and radioactive) by two Canadian companies (Phoenix Corporation and Geoterrex Limited) during the years 1979 and 1980. During the years 1992-1994 geochemical surveys were conducted in Aqaba complex and Wadi Araba through a joint venture between the NRA and the French company BRGM has included surveys over the entire basement exposed in South Jordan-the far north of the Shield [12] . The study area is located in the extreme southern part of Jordan between the (35 - 35. 75 PG) Attitude, at a distance of about 280 km from Amman. The map area is uninhabited except the city of Aqaba and a few villages and Bedouin communities along the main street linking (Figure 1). The study area is accessible through highway or The Dead Sea-Wadi Araba road. Abundant alluvial fans are available and reflect the tectonic activity along the fault of the Dead Sea on the Jordanian side. The pre-Cambrian granite rocks, representing the Arabian-Nubian Shield exposed in the north-west of the Arabian Peninsula and Jordan, where it ends at 30 km’s north of the Gulf of Aqaba on the west shoulder of the Wadi Araba, and along the eastern side of the Wadi Araba they constitute the mountains between Aqaba and Alqoirh in the north-east part through, Wadi Al Yutum, even disappear completely near the bottom of the Qa’a Al Disi area. Location of south Jordan sampling sites. The overall low strength results could be related to the micro internal deformation in the granite masses in the study area caused by the ground movements due to dissected strike-slip fault which running along the Jordan Rift Valley. (1959) Handbook of the Geology of Jordan. To Accompany and Explain the Three Sheets of the 1:250,000 Geological Map of Jordan East of the Rift by A. Government of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, 82. (1968) Geologie von Jordanien, Beitrage zur Regional Geologie der Erde. (1939) Report on the Water Resources of Transjordan and Their Development. (1951) The Geology and Mineral Resources of (Former) Transjordan. (1974) Geology of Jordan Contribution to the Regional Geology of the World. (1964) Geological and Petrological Investigations of the Igneous Rocks in the Area of Quweira, South Jordan. Report German Geological Mission in Jordan, 12 p. (1969) Modalbestand und petrochemie der granite von Aqaba-Quweira, SU djordanien. The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. (1990) The Geology, Geochemistry and Tectonic Setting of the Granitic and Associated Rocks in the Aqaba and Araba Complexes of Southwest Jordan. The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Natural Resources Authority, Geology Directorate, Amman. (1988) Petrography of the Plutonic Rocks of the Aqaba Complex, Jordan.
Read More ...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/natural-gypsum
https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/8824/phosphate-mines-in-jordan

